
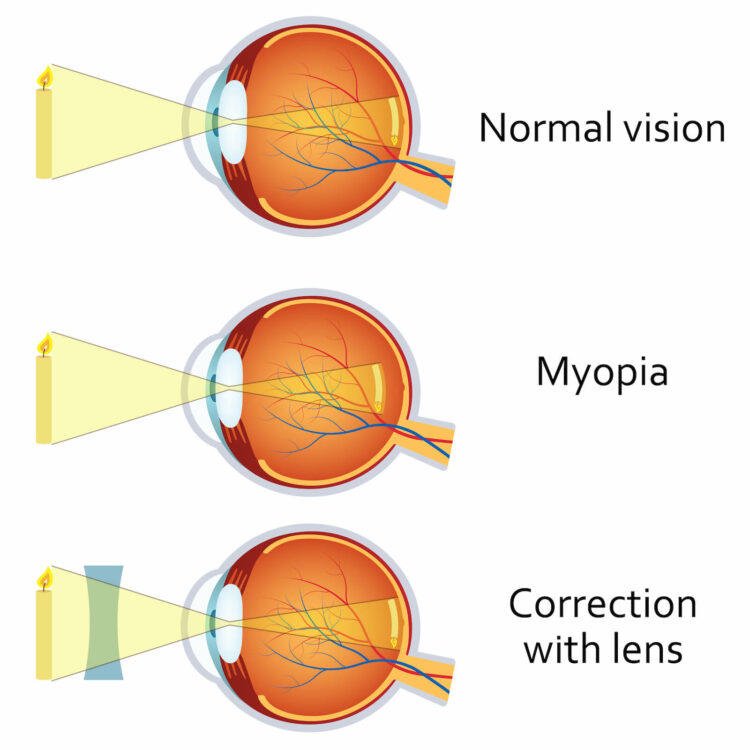
Myopia, commonly called nearsightedness, is a refractive error of the eye, meaning that the shape of the eye or its cornea improperly bends light as it enters the eye. This hinders your ability to focus. Myopia is the most common refractive error of the eyes, and is caused by several factors including eye strain, overuse, and genetic predisposition.
Nearsighted eyes are longer than normal. When light enters a nearsighted eye, it focuses to a point in front of the retina, where photoreceptors are located. As a result, nearsighted individuals are able to see nearby objects clearly, but have difficulty focusing on distant objects. In addition to having difficulty seeing distant objects such as road signs, a television screen, or a chalkboard, myopia can also cause eye strain, squinting, and headaches. Nearsighted individuals might also experience a sense of fatigue during athletic activities or while driving.
Inherited myopia develops during childhood, and can progressively worsen as the eyes grow until individuals reach about the age of 20. After the eyes have developed fully, myopia can continue to progress due to eye fatigue and eye strain from activities which require the eyes to be focused on nearby objects like reading and computer work. Individuals without inherited myopia can develop nearsightedness from overuse as well.
Myopia is usually diagnosed after the patient notices frequent headaches or difficulty seeing distant objects. After a comprehensive eye exam, an eye care professional will provide a myopia diagnosis. The severity of myopia has three classifications which depend on the strength of the prescription determined by an eye care professional: mild, moderate, and high.
Several treatment options exist for individuals with myopia. These include contact lenses, glasses, and refractive surgery. Glasses and contact lenses correct the refractive error in eyes by bending light before it enters the eye, allowing it to focus on the retina. Refractive surgery, like LASIK surgery, physically reshapes the eye to correct the refractive error, eliminating or reducing the need for corrective lenses.
In addition to these treatments, which are intended to correct nearsighted vision, there are also various therapies available to hinder or slow the progression of myopia in childhood. These treatments include multifocal corrective lenses, atropine eye drops, and orthokeratology. The course of treatment which an eye care professional recommends for each patient depends on the severity of the myopia.